Cheese Overview
Cheese is an ancient traditional fresh or fermented dairy product with a long history of production that is derived from the milk of various mammals. Cheese is mostly made from the milk of cows but also other mammals, including sheep, goats, buffalo, etc. Cow milk is commonly used for making cheese all over the world however buffalo milk can also be used for Cheese making with certain process modifications. The quality of raw milk used for cheese making determines the quality of resulting cheese.
Cheese is a milk concentrate (contains casein and fat). Cheese is a nutrient-dense dairy food, providing protein, fats, and minerals. The main components of cheese are water, milk fat, and milk proteins, predominantly casein. Milk doesn’t turn into delicious cheese on its own. Another important ingredient in cheese is a coagulant, which helps the milk turn into curds. The coagulant may be a type of acid or, more commonly, rennet. Rennet is an enzyme complex that is genetically engineered through microbial bioprocessing.
There are over 300 varieties of cheese produced in the U.S., most of which are made from cows’ milk. Cheese can be ripened (aged) by bacteria or mold or left unripened (fresh), such as cream cheese and cottage cheese. Cheese is categorized by its degree of hardness, and legal standards dictate the maximum moisture limits and minimum milk fat levels for those categories.
The standards include:
- Soft (e.g. Brie, ricotta, and feta);
- Semi-soft (e.g. blue, mozzarella, and provolone);
- Hard (e.g. cheddar, Gouda, and Swiss); and
- Very hard (e.g. parmesan and romano).
Traditionally, cheese was kept for months or sometimes even years for ripening and development of typical texture and flavour. Scientific development and research have accelerated the cheese ripening process and to achieve the desired texture and flavour in a very less time.
A tremendous proportion of the demand in the dairy and cheese industries comes from the popularity of frozen meals containing cheese, such as pizza, as well as from specialty, artisanal, and farmstead cheeses.
Specialty cheeses are regarded as having high quality and as being unique in some way, whether it is the processing method used or the presence of a distinct flavor. Artisan or artisanal cheeses are made in small batches, almost entirely by hand, and with as little mechanization as possible. Farmstead cheese is a type of artisanal cheese that is produced on the farm from milk obtained from the farmer’s animals only.
Cheese production business requires your time, effort, planning and a little capital. It is important to consider the type of cheese and milk that you will use. Invest on good quality supplies and equipment that can help you in the cheese making process.
Market Potential of Cheese Production Business
Cheese is a natural diary product that is healthy, has good nutritious value and high demand. Demand for organic cheese exceeds $6.5 billion in 2019 with a gradual increase every year.
The business is profitable requires moderate investment, inexpensive ingredients and basic equipment. Quality cheese requires good equipment, quality control and standardization.
Steps to follow to start a Profitable Cheese Production Business
-
Create a Business Plan
To begin a cheese production business you must do a proper market analysis and get an idea of your target market. Then do a proper business plan and feasibility study. You can even begin from scratch, or join a franchise or overtake an existing business.
While cheese is very popular, it would be helpful if you can estimate the market demand to see if it is sufficient enough. While the market for specialty foods and locally produced goods has grown over the years, but the dairy industry in your location may be quite competitive. Knowing the demand in your locality can be very helpful.
Next, get the information of the cheese-making process and distinguish different cheese items before composing your recipe. Attend trainings, symposiums and even have a tour in a cheese making plant to get more knowledge and information before deciding to enter in this venture. Register a business name, have insurance cover, and register the items. Understand what constitute premium cheese and marketing.
-
- Proper analysis of your target market
- Craft an appropriate business project and feasibility study
- Initiate from scratch or purchase an already existing business.
- Get the knowledge about the cheese-making step
- Differentiate the various cheese products
- Design your recipe
- Make sure you register the business name
- Avail insurance
- Register the product
- Marketing ideas.
2. Registration, license and permissions required to start Cheese Production Business in India
It is very important to consider this aspect of registration for your business no matter you plan for any size of your business. The process differs depending on your state’s laws. Additionally, as it comes under the food category, the Cheese manufacturing demands particular permission from the concerned government body. It is recommended to consult with a business consultant for operating the unit smoothly without any legal troubles.
Below is the list of licenses required before starting the Cheese Production Business in India
-
- Registration of firm
- GST registration
- Trade license
- Pollution certificate
- MSME/SSI registration
- EPI and ESI registrations
- Trademark
- FSSAI registration
- IEC code
- FPO act.
Business Entity: The first registration for any business is to register it as a business entity by knowing about the form of the organization. It could be as a sole proprietorship or a partnership or a limited liability partnership or a one-person company. This will help in availing a few benefits to the business and must, therefore, be selected carefully before registering the business at the Registrar’s office.
FSSAI registration: As Cheese is classified as the processing of food or food products and thus as per the definition requires an FSSAI registration. Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is meant for protecting and promoting public health by regulation and supervision of food safety hence FSSAI is a mandatory registration/license for the business. The FSSAI registration process is entirely online and quite easy to follow, once the documents are ready.
Shop Act or Trade License: As the Cheese business for example in Maharashtra, India requires applying for a Shop Act License from the local municipal authority to run the business. This license helps manage the working conditions along with working hours, leaves, wages, holidays, etc. of the employees and supports the business to run smoothly.
Udyog Aadhaar Registration: As the Cheese is categorized as a small business and hence it must be registered under Udyog Aadhaar which is a registration and recognition for MSMEs- micro, small, and medium enterprises.
GST Registration: Every business, including the Cheese, should associate with taxes at some point and for monitoring a single uniform taxation structure, the business should get a common GST number which stands for Goods and Service Tax.
BIS certification: Apart from these registrations the business should get BIS certification as well as tax liabilities.
No Objection Certificate from State Pollution Control Board: Cheese doesn’t cause any pollution so no clearance is needed, however, it is recommended to check it with the State Pollution Control Board of the locality where the business is established.
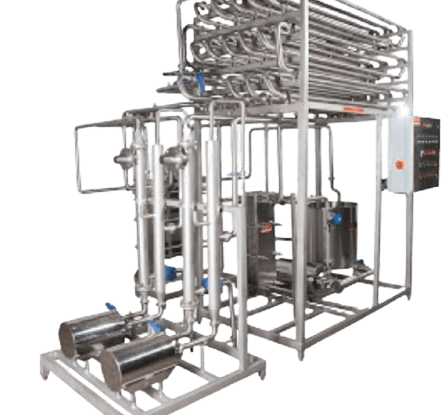
3. Machine and Equipment required for Cheese Production Business
The Cheese Production Plant is basically composed of:
-
- Milk Reception Section
- Cheese Vat
- Cheese Hoops
- Cheese Press (Pneumatically operated)
- Cheese Cutting Machine
- Cheese Sealing Machine
- Cheese Cold Room (Cold Chambers)
4. Cheese Production Business Set Up (Location)
Generally, you can begin a small-scale Cheese making business plant in a 100-150 sq. ft. area. However, space is based on the business size and the expected production capacity or yield in specific.
Choose the location properly. It is better to have space near to the industrial area. Additionally, you must check for a good water resource and an uninterrupted power supply. Check the transport availability provision as well. If you wish to keep a goods vehicle for logistic purposes then make sure you allocate a safe parking place.
5. Cost of Starting Cheese Production Unit (Investment cost)
If you are choosing any small-scale business in Cheese production then you must pay for raw materials specifically milk and other things such as packaging material and other things. If you are inaugurating a small-scale business then employees’ remuneration is also essential. The capital for small scale Cheese production business is Rs. 1 lakh. Additionally, on a large-scale basis, the equipment can be around 2.30 lakh rupees. The cost of raw material could be about Rs. 10,000. Therefore, the entire cost could be estimated to 1-1.5 lakh rupees.
For beginning the business, you must plan for the budget. You may charge around 150 to 200 rupees per kilogram in the market. Not only this, but you can also directly contact and have a network with restaurants and hotel industries.
6. Cheese Production Process
The cheese production is carried out from lactic acid fermentation of milk. By the enzymatic activity of rennin the coagulation of milk protein and formation of curd will take place. After the curd is formed it is heated and pressed to remove the watery part of the milk, salted and then ripened. The organisms responsible for the manufacturing of cheese are Lactobacillus lactis, Propionibacterium species. and Penicillium species.
The basic principles of cheese manufacturing involves the removal of water from milk with a consequent six to tenfold concentration of the protein, fat, minerals and vitamins by the formation of a protein coagulum that then shrinks to expel “whey”. The processes involved are- acidification, coagulation, cooking, salting, dehydration or syneresis, moulding (or shaping) and pressing, packaging and maturation or storage.
The cheese-making process primarily consists of fluid handling. The basic process of cheesemaking follows these steps:
-
- Standardize milk to make it as uniform as possible.
- Pasteurize or heat-treat milk to reduce the potential for spoilage. Time and temperature will vary based on the type of cheese.
- Cool the treated milk to a temperature that is optimal for culturing (typically 90 F) Again, the temperature depends on the type of cheese.
- Add starter bacterial ingredients and hold for approximately 30 minutes. The bacteria start to grow and fermentation begins. Fermentation lowers the pH of the cheese and develops the flavor.
- At the end of the prescribed time interval, Rennet or other enzymes are added to initiate the curdling process. Once these enzymes are added the curd is not disturbed for approximately 30 minutes. During this time it coagulates and continues to ferment.
- At this point in the process, the product is referred to as curd. As the curd reaches a specific pH (generally 6.4) it is cut into smaller pieces and heated to help separate liquid whey from the curd.
- When the liquid whey has been separated and is completely drained from the vats the remaining curd forms a mat. Once the mat is formed there are several operations that can occur depending on the type of cheese. Most often the curd is cut into sections. The size of the pieces is determined and piled on top of each other, an operation that is referred to as cheddaring. Cheddaring is also used to eliminate more whey.
The curd is left to continue fermenting until the desired pH is reached – generally between 5.1 – 5.5. While the curd is fermenting, the mats begin a process called knitting, in which the cheese forms a tighter matted structure. In place of knitting, stretching and pressing may be used, which produce cheese with different textures and flavors. Very soft cheese such as cottage cheese tends to skip this step.
-
- Once the curd mats are processed the cheese will be dry salted or brined.
- Following the salting step, the curd pieces are placed into forms and pressed into blocks to form the cheese. Depending on the sophistication of the manufacturing operation this process may be either manual or automated. A wide range of containers are used to form the cheese such as wood, plastic, stainless steel, or other materials. The shape of the container will vary as well.
- In large industrial cheese-making operations, the curd is formed into blocks using equipment called block towers. Round blocks are referred to as wheels, but shapes and sizes of the blocks can vary.
- Once blocks are formed they are typically sent to a controlled environment area for a process called aging. During the aging process, the cheese develops the flavor and texture profiles. The length of the aging process depends on the type and style of the cheese.
- The last stage in the manufacturing process of Cheese is called packaging. In this process, the packaging is automatically done by the machine which has a ribbon of flat packaging cardboard threaded into it.
Fig. The general processing flowchart of natural cheeses
7. Marketing and Branding of your Cheese
Cheese products are having huge demand and thus marketing them is relatively simple. Sell the product in the farmers market, or supermarkets and grocery shops. Sell to hotels, top-class restaurants, delicatessens, food joints.
Another way is to initiate an artisan cheese shop and sell directly to people. Use electronic media, print, social platforms or you can even own a website to promote the products and publicize them to the target market.
As the Cheese is an FMCG product, it must have extensive advertising and product promotion methodology. And it is recommended to have an organized marketing team. Select a trendy and memorable name for your product. Prepare the label properly. Advertisements in the electronic media and FM channels are very essential in promoting this type of item. In addition to that, try to keep your product in retail stores as much as possible in your area. Supermarkets and malls are also the best choices for selling the product.
Register an easy and catchy name to remember the name for product branding. Add product brand name, product description, logo, content, net weight per kg, and preparation ingredients on the packet.
Explore
Related Products