Introduction of Butter and Ghee (Clarified Butter)
- Butter is a dairy product made from separating whole milk or cream into fat and buttermilk. This process of separating is known as churning. The fat is compressed and chilled into blocks of butter.
- Butter contains up to 80% butterfat which is solid when chilled and at room temperature. Butter consists of butterfat, milk proteins and water. Butterfat is a mixture of triglyceride, an ester derived from glycerol and fatty acids which vary in different types of triglycerides
- Butter is essentially the fat of milk. It is essentially a water-in-oil emulsion and is usually made from sweet cream and is salted. Salt less (sweet) butter is also available in the market. Butter can also be made from acidulated or bacteriologically soured cream. Commercial butter can be produced from both sweets as well as cultured cream.
- Butter comes in two forms salted and unsalted (sweet). Unsalted butter has a shelf life of around 3 months refrigerated because it contains no preservatives. Salted butter has a longer shelf life (up to 5 months) because salt acts as a preservative. However, salt can overpower the sweet flavor of the butter and can also mask any odors. The amount of salt added to salted butter can vary from manufacturer to manufacturer.
- Butter is manufactured from dairy cream using a churning process. The cream is produced by passing milk through a separator, which divides the incoming milk into skim milk (0.1% milk fat) and cream (35-40% milk fat).
Cream is churned until small butter grains form in buttermilk. The buttermilk is drained and the churning process continues until the grains are kneaded together. Salt is typically added and this adds flavour to the butter and also enhances its shelf-life. It requires about twenty litres of whole milk to produce one kilogram of butter. - The churning process results in a water-in-oil emulsion. The final product is around 80% milk fat, and 16% water in the form of very tiny droplets. The smooth texture of butter is closely linked to the working (kneading) process.
- In addition to milk fat and water, normal butter contains salt (1.5-2.0%), trace amounts of protein, calcium, phosphorous, and various fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, and E). Butter should have a uniform colour, and a smooth consistency so that it is easy to spread and readily melts on the tongue.
- Ghee accounts for about 45% of the total milk produced in India. Ghee is clarified butterfat and contains about 99% of milk fat. Ghee from buffalo milk has no color, unlike ghee from cattle, which is golden yellow due to the presence of carotenoids as stated earlier. Ghee is the only source of animal fat in the vegetarian diet of the human population in India.
- Ghee is a type of clarified butter that contains fewer dairy proteins than regular butter. Ghee is a form of highly-clarified butter that is traditionally used in Asian cooking. Like butter, ghee is typically made from cow’s milk. Ghee is made by melting regular butter. The butter separates into liquid fats and milk solids. Once separated, the milk solids are removed, which means that ghee has less lactose than butter.
- Ghee has a slightly higher concentration of fat than butter and more calories. One tablespoon of ghee has about 120 calories, whereas one tablespoon of butter has about 102 calories.
- India is the world’s largest producer and consumer of milk and dairy products. Ghee currently controls the second largest market share in terms of revenue in the Indian market. With the growth of the organized sector of the dairy industry and establishment of modern dairy plants, the emphasis has shifted to conducting investigations on newer and larger-scale methods of ghee manufacture which could profitably be adopted for routine ghee production by these dairies instead of the desi method used in the dairy.
Health Benefits of Ghee
- Ghee is rich in healthy fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamins A, D, E, and K. Actually, these vitamins are important for promoting bone and brain health, and for boosting the immune system. Ghee is the richest source of animal fat in the vegetarian diet. Actually, it supplies 9 K. calorie energy/gm. It has long keeping quality under tropical storage conditions.
- In addition to that, ghee converts fiber into butyric acid, which is beneficial to intestinal bacteria. Also, it helps to increase appetite, fostering better health and weight loss. Ghee cooks at a higher point than almost any other oil. That is why it won’t break into free radicals like other ones. Free radicals can potentially be harmful to one’s health
Is Ghee Business Profitable?
- Already there is a wide market for ghee. It is a popular FMCG item. Ghee represents the second-largest consumed dairy product in the Asian countries, after liquid milk. Additionally, the demand is growing rapidly throughout the world. India is the world’s largest producer of buffalo and cow milk and consequently also the largest producer and consumer of ghee. It is very fragrant with a rich nutty taste and represents the second largest consumed dairy product in India, after liquid milk.
- Basically, the population growth, health benefits, increasing disposable incomes, and penetration in newer markets currently represent some of the key factors driving the demand for this product. Apart from this, factors such as increasing population, urbanization rates, improved cold supply chain and growing deep freezer penetration are also influencing the market growth.
- This product is consumed in every household and there is always a significant demand in both rural as well as in urban sector. So to sum up, we can say it is a highly lucrative market for starting up an organized ghee manufacturing business.
7 steps to start a profitable Ghee Manufacturing Business
-
Market Research & Business Plan
First of all, you need to conduct a market study at your location. There are several specific types of ghee are available in the market. Broadly these are cow milk ghee and non-cow milk ghee. Also, ghee comes in different flavors.
So, you need to understand the specific demand for different types of ghee. In addition to that identify the established ghee manufacturing brands in your area. Check the packing and price. These all will help you in crafting the business plan and initiating the manufacturing operation.
Finally, you need to craft the business plan or project report. Typically, a business plan includes executing a summary, financial analysis, project cost, and marketing plan. If you want to start a large-scale operation, you can consider applying for bank finance.
2. Business Registration & License
Regardless of the size of your business, you need to get business registration. Definitely, the process varies depending on your state’s regulations. Additionally, as it comes under food items, ghee manufacturing demands specific permission from the concerned department. It is advisable to consult with a business consultant for establishing the unit smoothly.
The two licenses that you need to procure to start a ghee manufacturing business are the FSSAI license and GST Registration.
3. Space Requirement and Set Up for Ghee Manufacturing Business
- In general, you may start a small-scale ghee manufacturing company in a 100-150 sq. ft. space. However, space is determined by the size of the firm and the estimated production capacity or output.
- Choose a suitable place. It is preferable to have space close to the industrial sector. It would be best to look for a decent water supply and an uninterrupted electricity supply. Examine the transportation availability provision.
- If you have a big dairy farm then you must go for large scale ghee manufacturing plant. Moreover, if you are leading a small scale ghee plant than, you should fix the small scale ghee manufacturing plant in a covered space. In addition, you have to select the location carefully where you actually want to set ghee milking plant. These are not only factors which you have to consider while installing this plant, additionally, you also ensure the good water resource there and must check the transport facility in order to deliver the ghee to other places.
4. Investment Cost
If you choose a small scale business in ghee manufacturing, you must pay for raw materials, notably milk, and additional items like packaging material and other things. Employee compensation is significant when starting a small size firm. The initial investment for a small-scale ghee producing firm is Rs. 1 lakh. Furthermore, the equipment might cost approximately 2.30 lakh rupees on a large scale. The raw material cost might be about Rs. 10,000. As a result, the total cost may be calculated at 1-1.5 lakh rupees.
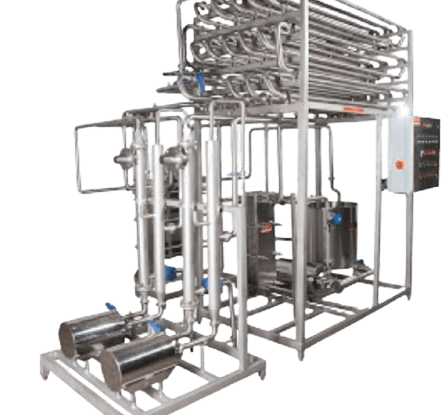
5. Machinery/Equipment’s for Ghee Manufacturing Business
Essential machinery requirements are as follows
-
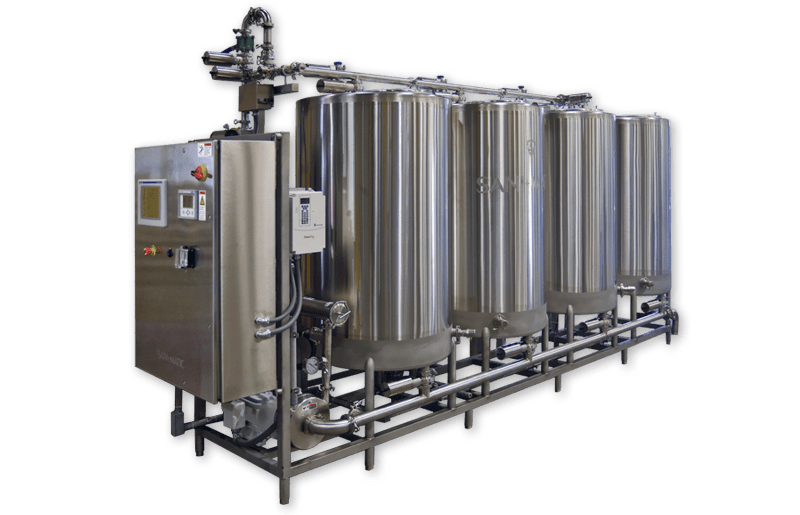
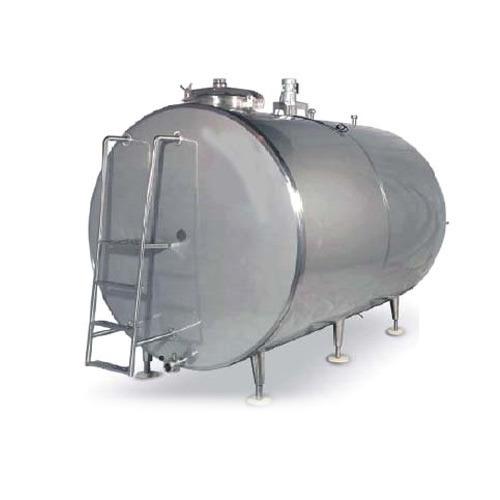
- Milk Storage Tank
- Balance Tanks
- Milk Homogenizer
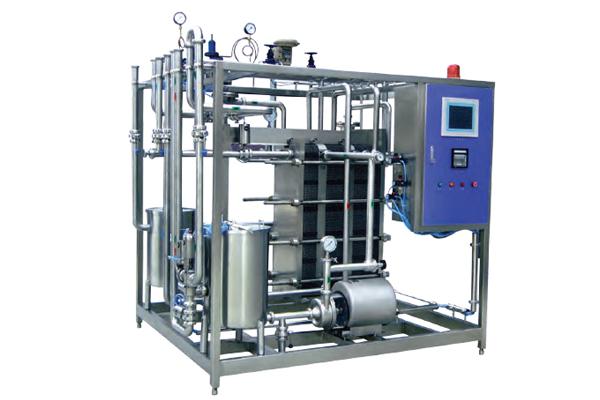
- Milk Pasteurizer
- Cream Separator
- Boiler
- Chiller
- IBT Type chilling machine
- Butter Churning Machine
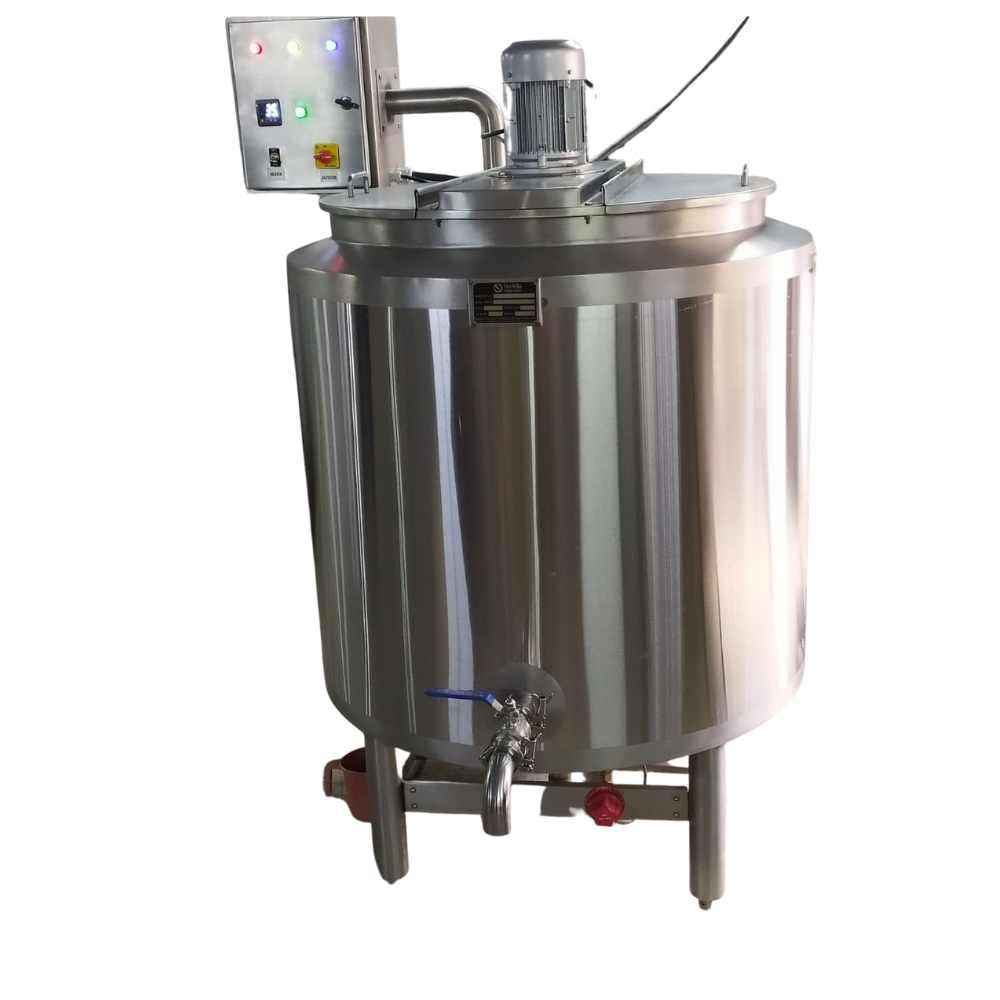
- Ghee Boiling Kettle
- Pouch Filling Machine
- Pumps
- Piping
- Electrical Panel.
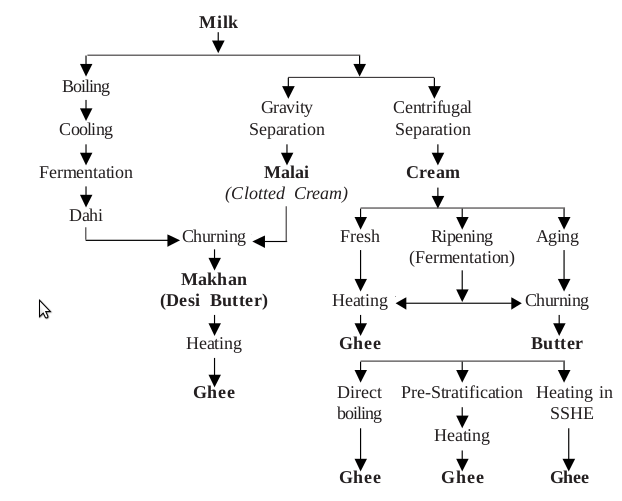
6. Manufacturing Process (Ghee Production Overview)
- Before the main processing of milk, milk is purchased from a vendor and held in storage tanks. A boiler is used to create steam, which is then used in different processes throughout the plant, including heating milk and milk products as needed.
- This steam is initially used in the pasteurizer to heat the milk for pasteurization; after an appropriate holding time, the milk is sent to another holding tank, which stores the milk before cooling, and it is necessary to reduce the load on the milk cooler and provide a constant feed to the milk cooler.
- After cooling, milk is stored in a holding tank, from which it is supplied to a milk homogenizer, which ensures uniform globule size in milk. Thereafter which, milk is stored in a balance tank, from which it is fed to a cream separator, which essentially extracts cream from milk and stores it in another balance tank. In contrast, toned milk is supplied to a pouch filling machine, which packs the toned milk into packets of appropriate quantity and is then stored.
- On the other hand, the cream is chilled in a separate chiller to a temperature of 4 to 5 degrees Celsius. After that, the cream is fed into the butter churning equipment.
- The butter churning machine extracts butter from cream, which is then fed into a heating vessel, which warms the butter to produce ghee. This ghee is fed into another pouch packaging machine, which packs the ghee into proper-sized packets, kept in a cool area until they are sold.
- The manufacturing process comprises two steps: separation of cream from milk and extraction of ghee from the cream. Also, you can sell the cream less milk as toned milk. You can set up a pasteurization plant to increase the shelf life of the milk and to separate cream through an automated process.
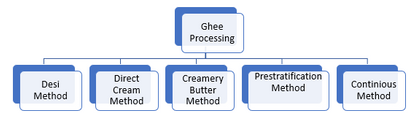
There are in total five different methods for producing ghee.
To know more details about the production of ghee and butter in depth, kindly visit our blog- https://techqueng.blogspot.com/2022/08/insights-on-ghee-butter-and-its.html
7. Ghee Marketing & Distribution
As the ghee is an FMCG product, it demands extensive advertising and product promotion strategy. And it is better to have an organized marketing team. Select a catchy and memorable name for your product. Prepare the label carefully.
Advertisement in the electronic media and FM channels are useful in promoting this type of product. In addition to that, make your product available in retail stores as much as possible in your locality. Supermarkets and malls are also the options for selling the product.
Basically, ghee manufacturing is a working capital-intensive business. So, proper cost analysis and financial planning are necessary for long-term success.
Explore
Related Products